Linked List - Top Interview Questions[EASY] (3/9) : Python
Linked List
Linked List problems are relatively easy to master. Do not forget the Two-pointer technique, which not only applicable to Array problems but also Linked List problems as well.
Another technique to greatly simplify coding in linked list problems is the dummy node trick.
We recommend:
- Reverse Linked List,
- Merge Two Sorted Lists
- Linked List Cycle.
For additional challenge, solve these problems recursively:
Reverse Linked List,
Palindrome Linked List
Merge Two Sorted Lists.
| iterative | recursive | |
| Delete Node in a Linked List | 1/4 | |
| [*] Reverse Linked List, | 1/4 | |
| [*] Merge Two Sorted Lists | 1/4 | |
| [*] Linked List Cycle. | 1/4 | |
| [*] Palindrome Linked List | ||
[*] important
237. Delete Node in a Linked List
leetcode.com/problems/delete-node-in-a-linked-list/
Easy
18227806Add to ListShare
Write a function to delete a node in a singly-linked list. You will not be given access to the head of the list, instead you will be given access to the node to be deleted directly.
It is guaranteed that the node to be deleted is not a tail node in the list.
Example 1:
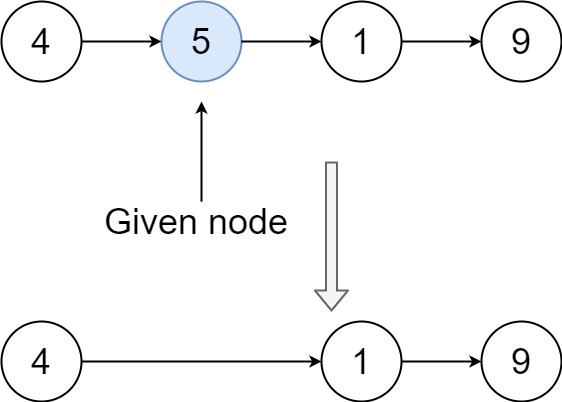
Input: head = [4,5,1,9], node = 5 Output: [4,1,9] Explanation: You are given the second node with value 5, the linked list should become 4 -> 1 -> 9 after calling your function.
Example 2:
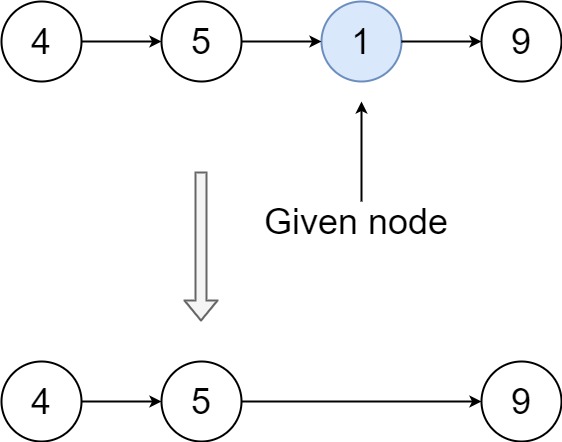
Input: head = [4,5,1,9], node = 1 Output: [4,5,9] Explanation: You are given the third node with value 1, the linked list should become 4 -> 5 -> 9 after calling your function.
Example 3:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4], node = 3 Output: [1,2,4]
Example 4:
Input: head = [0,1], node = 0 Output: [1]
Example 5:
Input: head = [-3,5,-99], node = -3 Output: [5,-99]
Constraints:
- The number of the nodes in the given list is in the range [2, 1000].
- -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
- The value of each node in the list is unique.
- The node to be deleted is in the list and is not a tail node
Solution
Approach: Swap with Next Node [Accepted]
The usual way of deleting a node node from a linked list is to modify the next pointer of the node before it, to point to the node after it.
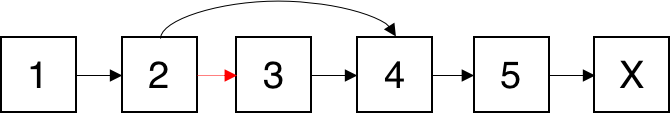
Since we do not have access to the node before the one we want to delete, we cannot modify the next pointer of that node in any way. Instead, we have to replace the value of the node we want to delete with the value in the node after it, and then delete the node after it.



Because we know that the node we want to delete is not the tail of the list, we can guarantee that this approach is possible.
Java
public void deleteNode(ListNode node) { node.val = node.next.val; node.next = node.next.next; }
Complexity Analysis
Time and space complexity are both O(1)O(1).
Analysis written by: @noran
class Solution:
def deleteNode(self, node):
"""
:type node: ListNode
:rtype: void Do not return anything, modify node in-place instead.
"""
node.val = node.next.val
node.next = node.next.next
19. Remove Nth Node From End of List
leetcode.com/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/
class Solution:
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: ListNode, n: int) -> ListNode:
first = second = head
for _ in range(n):
first = first.next
if not first:
return head.next
while first.next:
first = first.next
second = second.next
second.next = second.next.next
return head
내코드
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: ListNode, n: int) -> ListNode:
dummy = ListNode(-1)
dummy.next = head
slow = dummy
fast = dummy
while n >= 0:
fast = fast.next
n -= 1
while fast:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
slow.next = slow.next.next
return dummy.next
while 을 for 로 발전시킴
class Solution:
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: ListNode, n: int) -> ListNode:
dummy = ListNode(-1)
dummy.next = head
slow = fast = dummy
for _ in range(n+1):
fast = fast.next
while fast:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
slow.next = slow.next.next
return dummy.next
leetcode.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
prev, curr = None, head
while curr:
curr.next, prev, curr = prev, curr, curr.next
return prevclass Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if not head or not head.next:
return head
p = self.reverseList(head.next)
head.next.next, head.next = head, None
return p
leetcode.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/

class Solution:
def mergeTwoLists(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
prehead = ListNode(-1)
prev = prehead
while l1 and l2:
if l1.val <= l2.val:
prev.next = l1
l1 = l1.next
else:
prev.next = l2
l2 = l2.next
prev = prev.next
prev.next = l1 if l1 is not None else l2
return prehead.next
234. Palindrome Linked List
leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-linked-list/solution/
class Solution:
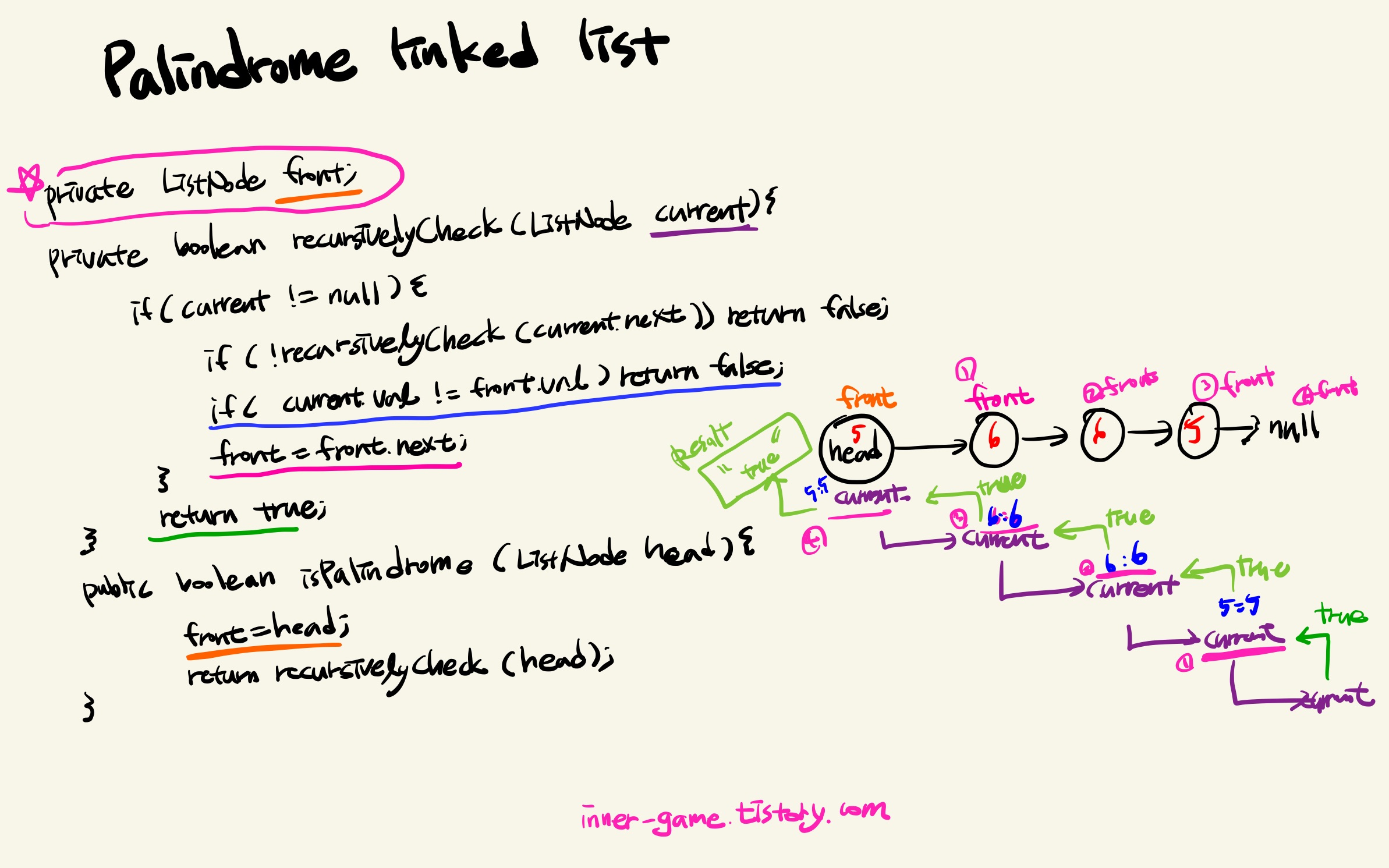
def isPalindrome(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:
self.front = head
def recursively_check(current_node = head):
if current_node is not None:
if not recursively_check(current_node.next):
return False
if self.front.val != current_node.val:
return False
self.front = self.front.next
return True
return recursively_check()다른방법은 공간복잡도 O(1)이 있긴한데...아직 못봄
leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/
class Solution:
def hasCycle(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:
if head is None:
return False
slow = head
fast = head.next
while slow != fast:
if fast is None or fast.next is None:
return False
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
return True

Array - Top Interview Questions[EASY] (1/9) : Java
String - Top Interview Questions[EASY] (2/9) : Java
Linked List - Top Interview Questions[EASY] (3/9) : Java
Trees - Top Interview Questions[EASY] (4/9) : Java
Sorting and Searching - Top Interview Questions[EASY] (5/9) : Java
Dynamic Programming - Top Interview Questions[EASY] (6/9) : Java
Design - Top Interview Questions[EASY] (7/9) - Java
Array - Top Interview Questions[EASY] (1/9) : Python
String - Top Interview Questions[EASY] (2/9) : Python
Linked List - Top Interview Questions[EASY] (3/9) : Python
Trees - Top Interview Questions[EASY] (4/9) : Python
Sorting and Searching - Top Interview Questions[EASY] (5/9) : Python
Dynamic Programming - Top Interview Questions[EASY] (6/9) : Python
Design - Top Interview Questions[EASY] (7/9) - Python





