자바 치트 시트(cheat sheet) - 버전 11
● 헬로우월드 출력하기 - 디버깅 출력할때도 중요함
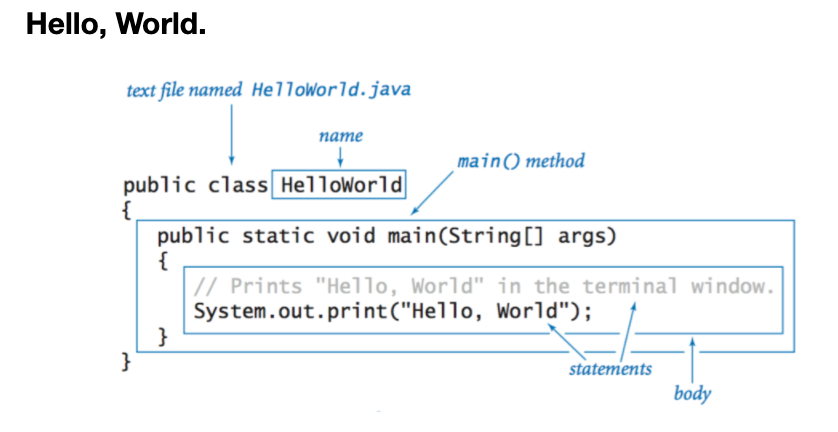

그리고 다른 프린팅 옵션들도 좀 정리해야함.

● 에디팅, 컴파일링, 실행 의 개념
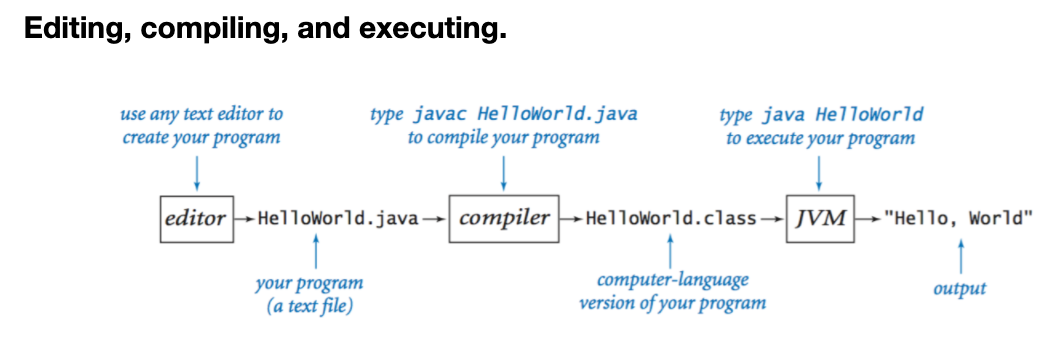
editor: 우리가 프로그램을 마들기 위해 코드를 입력함
-> HelloWorld.java 라는 파일이 생김
compiler: javac HelloWorld.java 커맨드라인에 입력하면 컴파일이 됨
-> HelloWorld.class 라는 컴퓨터언어 버전의 프로그램이 생성됨
JVM: java HelloWorld를 커맨드라인에서 입력하면, 프로그램이 실행되고 결과가 출력됨
-> "Hello, World'를 출력하기로 한 프로그램이었으므로 그렇게 실행됨.
● 내장 데이터 타입들
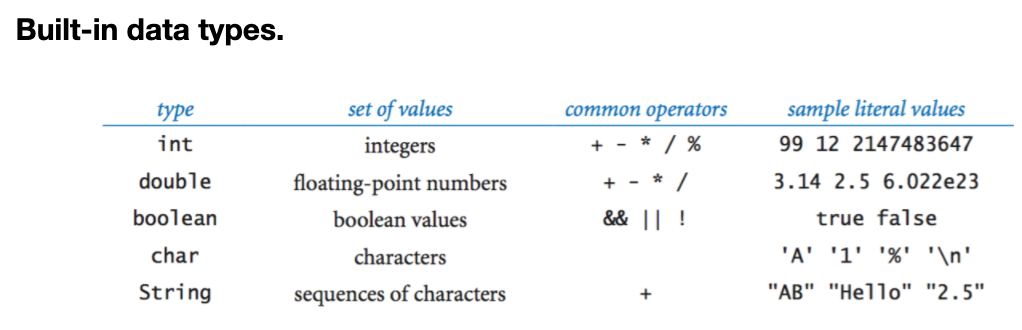
5가지가 있다. int, double, boolean, char, string
long 이런것은 왜 없는것인가?
● 선언과 정의

int a, b; // declaration statement
a = 1234; // variable name and literal (리터럴)
b = 99; // assignment statement
int c = a + b; // inline initialization statement
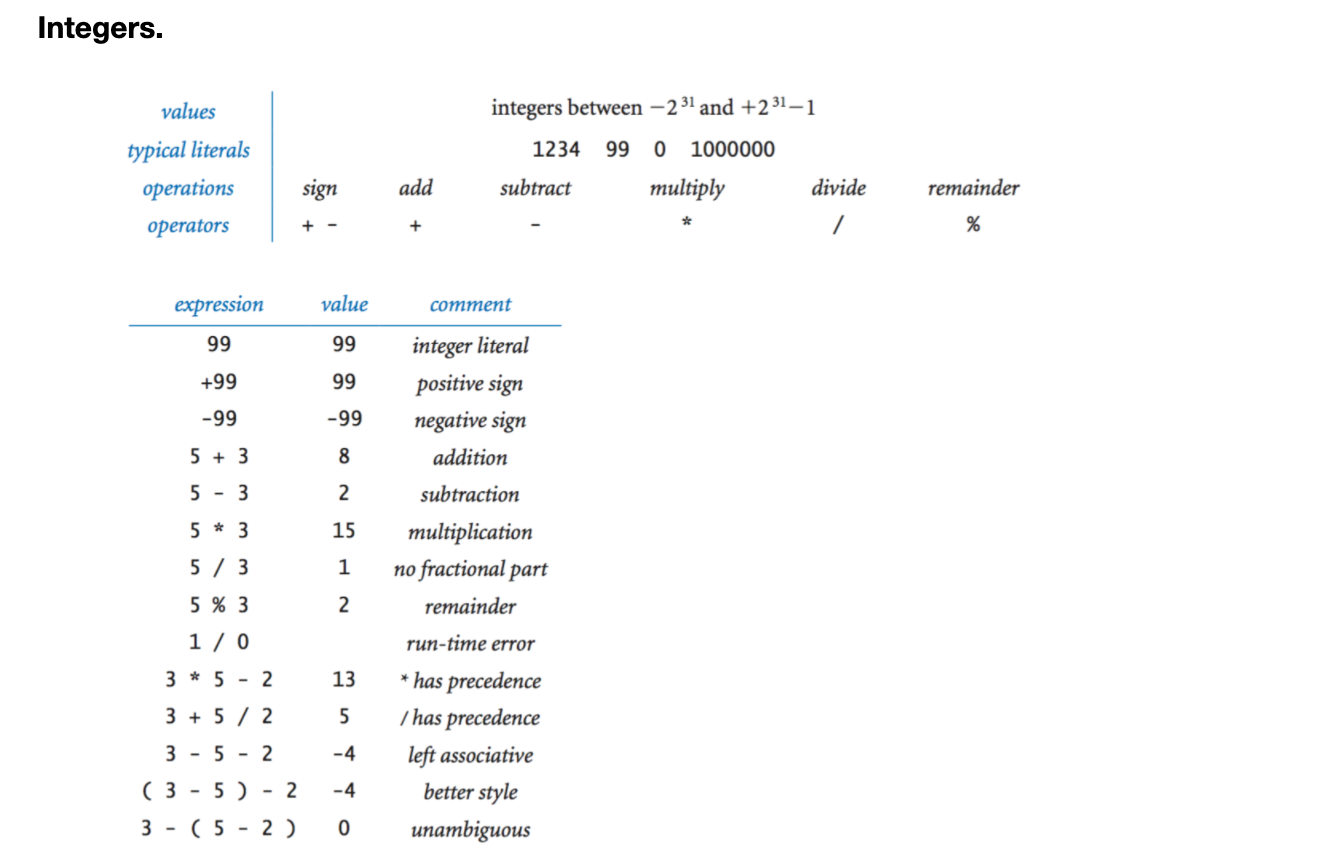
● 정수형. Integers
-2^31 ~ 2^31-1
● 부동소수점형. floating-point numbers
실수형과의 차이는?

● 불리언 booleans

● Comparision operatiors. 비교 연산자.
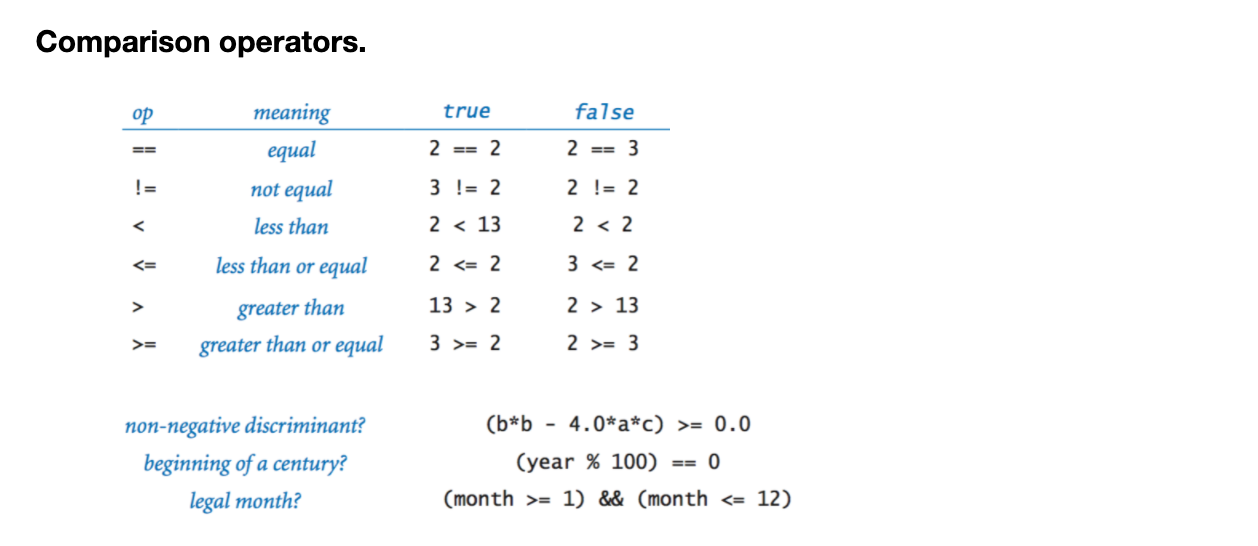
== equal, != not equal, < less than, <= less than or equal, > greater than, >= greater than equal
non-negative discriminant는 무슨말인지...양수인지 본다는거 같은데 a,b,c의 뜻을 모르겠네.
● Parsing command-line arguments

int a = Integer.parseInt("234");
double a = Double parseDouble("23");
long a = Long.parseLong("234");
-
int: By default, the int data type is a 32-bit signed two's complement integer, which has a minimum value of -231 and a maximum value of 231-1. In Java SE 8 and later, you can use the int data type to represent an unsigned 32-bit integer, which has a minimum value of 0 and a maximum value of 232-1. Use the Integer class to use int data type as an unsigned integer. See the section The Number Classes for more information. Static methods like compareUnsigned, divideUnsigned etc have been added to the Integer class to support the arithmetic operations for unsigned integers.
-
long: The long data type is a 64-bit two's complement integer. The signed long has a minimum value of -2^63 and a maximum value of 263-1. In Java SE 8 and later, you can use the long data type to represent an unsigned 64-bit long, which has a minimum value of 0 and a maximum value of 2^64-1. Use this data type when you need a range of values wider than those provided by int. The Long class also contains methods like compareUnsigned, divideUnsigned etc to support arithmetic operations for unsigned long.
-
float: The float data type is a single-precision 32-bit IEEE 754 floating point. Its range of values is beyond the scope of this discussion, but is specified in the Floating-Point Types, Formats, and Values section of the Java Language Specification. As with the recommendations for byte and short, use a float (instead of double) if you need to save memory in large arrays of floating point numbers. This data type should never be used for precise values, such as currency. For that, you will need to use the java.math.BigDecimal class instead. Numbers and Strings covers BigDecimal and other useful classes provided by the Java platform.
-
double: The double data type is a double-precision 64-bit IEEE 754 floating point. Its range of values is beyond the scope of this discussion, but is specified in the Floating-Point Types, Formats, and Values section of the Java Language Specification. For decimal values, this data type is generally the default choice. As mentioned above, this data type should never be used for precise values, such as currency.

출처: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/java/nutsandbolts/datatypes.html
● Math Library 수학 라이브러리

abs, max, min,
sin, cos, tan,
toRadians, toDegrees
exp, log, pow, round,
random, sqrt
E, PI
E가 뭐더라...
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/Math.html
● Java Library Calls
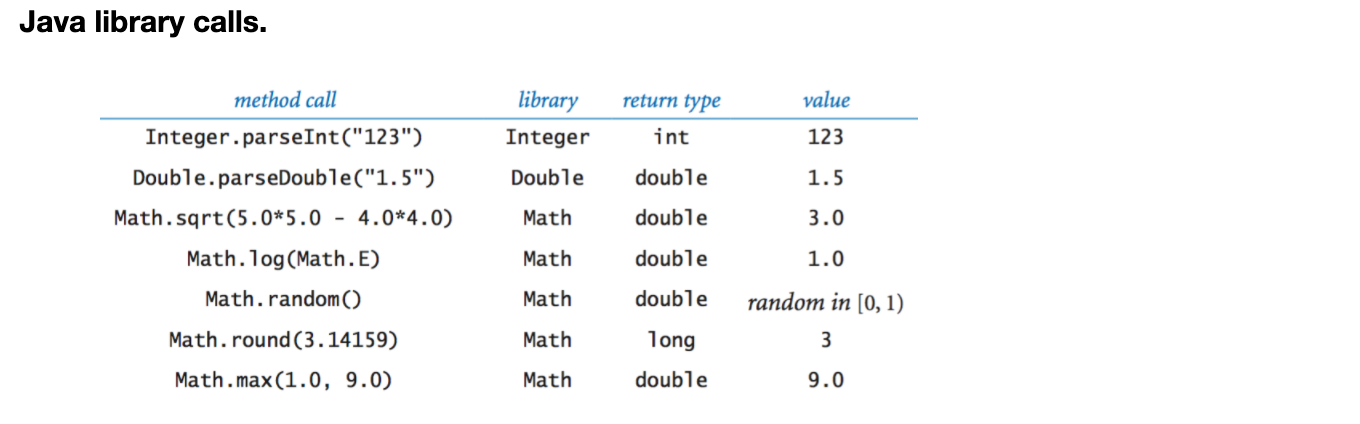
전부 위에서 다룬 것들이라서 패스.
● Java Type conversion

처음 알고리즘대회 나갈때는 10^9 까지만 다룰수 있는 int에 대해서 어떻게 처리해야할지 막막할때가 있다.
덧셈 하기 직전에 처리해주면 된다.
● Java Anatomy of an if statement

● If and if-else statements
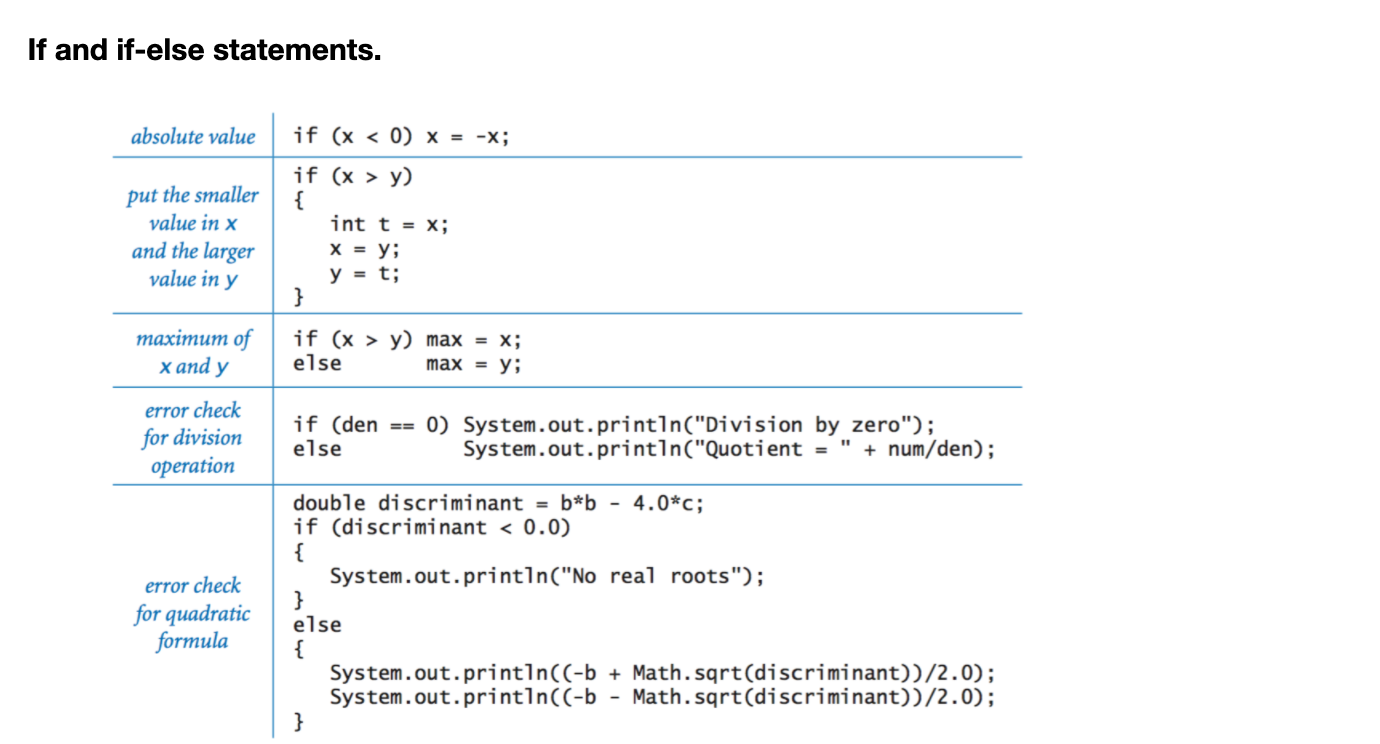
특별한것은 없는것 같다.

● Anatomy of a while loop






● Arrays

드디어 배열이 나왔다.

이부분이 배열에서는 가장 중요한 배열 처리 부분이다.
- 배열 생성할때
double[] a = new double[5];
for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
a[i] = Math.random();
}
double max = Double.NEGATIVE_INFINITY;
요거 자료형별로 쓰는 방법 암기해야함.
- 배열 역으로 바꾸기
for(int i = 0; i < n/2; i++) {
double temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[n-1-i];
a[n-1-i] = temp;
}
이런 인덱스들도 바로바로 활용할수 있도록 암기 필요

요것도 암기해버려야함
a[r][c] 라는것을 알아야하고, r 과 c 를 구하는 방법은
int numOfR = arr.length;
int numOfC = arr[r].length;
전체출처: https://introcs.cs.princeton.edu/java/11cheatsheet/





