LCA ( Lowest Common Ancestor )
리트코드에서 공통조상찾기 문제를 풀어봅시다.
leetcode.com/problemset/all/?search=lca
235. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree
leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-search-tree/
진정한 LCA 문제라기 보다는, BST의 특성을 이용해 값을 기준으로 부모노드의 위치를 찾아가는 문제.
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode':
parent_val = root.val
p_val = p.val
q_val = q.val
if p_val > parent_val and q_val > parent_val:
return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
elif p_val < parent_val and q_val < parent_val:
return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
else:
return root
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode':
p_val = p.val
q_val = q.val
node = root
while node:
parent_val = node.val
if p_val > parent_val and q_val > parent_val:
node = node.right
elif p_val < parent_val and q_val < parent_val:
node = node.left
else:
return node
236. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree
leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/
3개 다 O(N) O(N) 이긴 하지만..
Approach 1: Recursive Approach
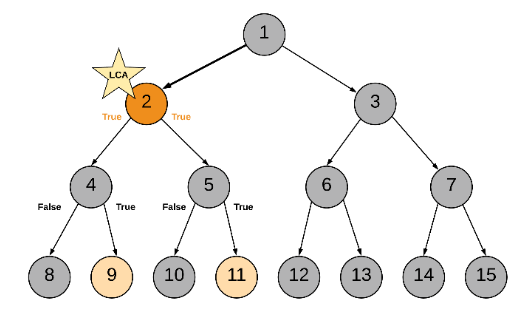
class Solution:
ans = 0
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode':
def recurse_tree(current_node):
if not current_node:
return False
left = recurse_tree(current_node.left)
right = recurse_tree(current_node.right)
mid = current_node == p or current_node == q
if mid + left + right >= 2:
self.ans = current_node
return mid or left or right
recurse_tree(root)
return self.ans
Approach 2: Iterative using parent pointers
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode':
stack = [root]
parent = {root: None}
while p not in parent or q not in parent:
node = stack.pop()
if node.left:
parent[node.left] = node
stack.append(node.left)
if node.right:
parent[node.right] = node
stack.append(node.right)
ancestors = set()
while p:
ancestors.add(p)
p = parent[p]
while q not in ancestors:
q = parent[q]
return q
Approach 3: Iterative without parent pointers
In the previous approach, we come across the LCA during the backtracking process. We can get rid of the backtracking process itself. In this approach we always have a pointer to the probable LCA and the moment we find both the nodes we return the pointer as the answer.
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
BOTH_PENDING = 2
LEFT_DONE = 1
BOTH_DONE = 0
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode':
stack = [(root, Solution.BOTH_PENDING)]
one_node_found = False
LCA_index = -1
while stack:
parent_node, parent_state = stack[-1]
if parent_state != Solution.BOTH_DONE:
if parent_state == Solution.BOTH_PENDING:
if parent_node == p or parent_node == q:
if one_node_found:
return stack[LCA_index][0]
else:
one_node_found = True
LCA_index = len(stack) - 1
child_node = parent_node.left
else:
child_node = parent_node.right
stack.pop()
stack.append((parent_node, parent_state - 1))
if child_node:
stack.append((child_node, Solution.BOTH_PENDING))
else:
if one_node_found and LCA_index == len(stack) - 1:
LCA_index -= 1
stack.pop()
return None
1123. Lowest Common Ancestor of Deepest Leaves
leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-deepest-leaves/
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def lcaDeepestLeaves(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
def dfs(root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
if not root:
return (0, None)
h1, lca1 = dfs(root.left)
h2, lca2 = dfs(root.right)
if h1 > h2: return h1+1, lca1
if h1 < h2: return h2+1, lca2
return h1 + 1, root
return dfs(root)[1]
leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree-ii/
leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree-iii/
leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree-iv/
leetcode.com/problems/smallest-common-region/





