340. Longest Substring with At Most K Distinct Characters
leetcode.com/problems/longest-substring-with-at-most-k-distinct-characters/
Given a string s and an integer k, return the length of the longest substring of s that contains at most k distinct characters.
Example 1:
Input: s = "eceba", k = 2 Output: 3 Explanation: The substring is "ece" with length 3.
Example 2:
Input: s = "aa", k = 1 Output: 2 Explanation: The substring is "aa" with length 2.
Constraints:
- 1 <= s.length <= 5 * 104
- 0 <= k <= 50
Video Solution
Solution Article
Approach 1: Sliding Window + Hashmap.
Intuition
We could take some inspiration from a simpler problem called longest substring with at most two distinct characters.
To solve the problem in one pass let's use here sliding window approach with two set pointers left and right serving as the window boundaries.
The idea is to set both pointers in the position 0 and then move right pointer to the right while the window contains not more than k distinct characters. If at some point we've got k + 1 distinct characters, let's move left pointer to keep not more than k + 1 distinct characters in the window.
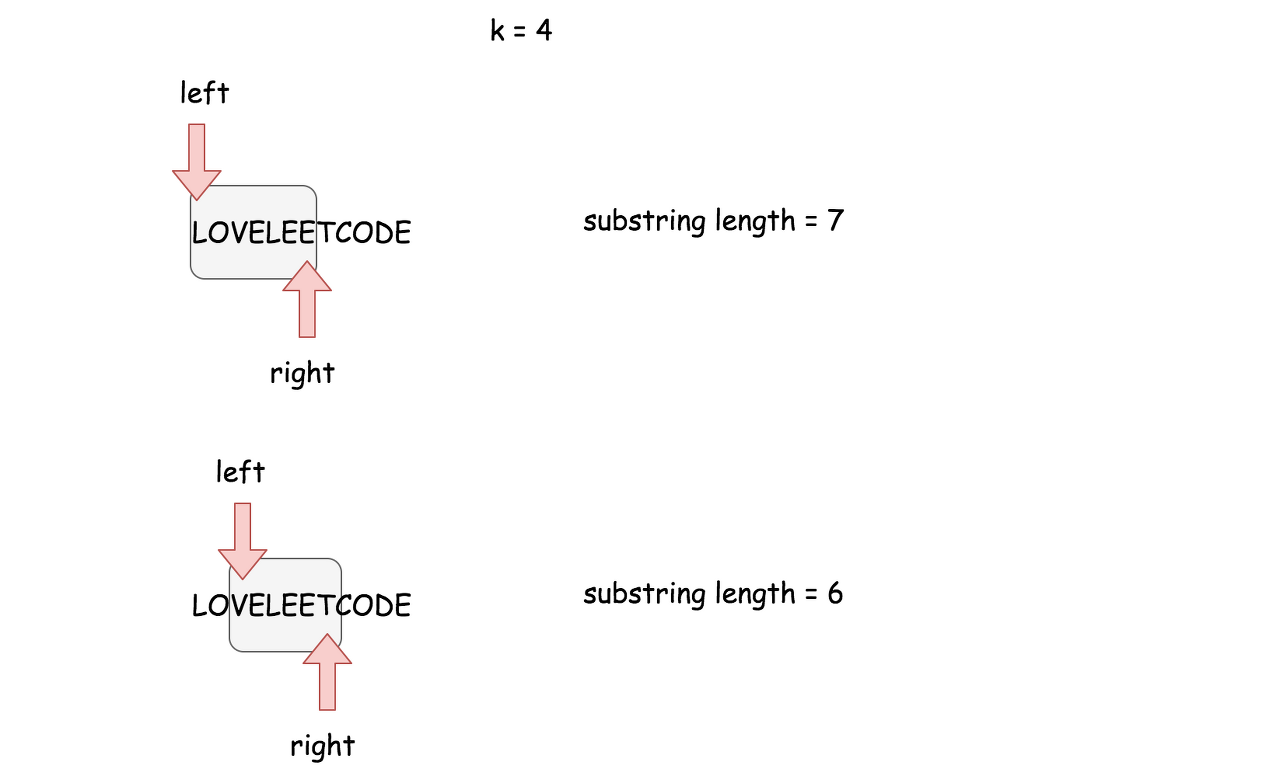
Basically that's the algorithm : to move sliding window along the string, to keep not more than k distinct characters in the window, and to update max substring length at each step.
There is just one more question to reply - how to move the left pointer to keep only k distinct characters in the string?
Let's use for this purpose hashmap containing all characters in the sliding window as keys and their rightmost positions as values. At each moment, this hashmap could contain not more than k + 1 elements.
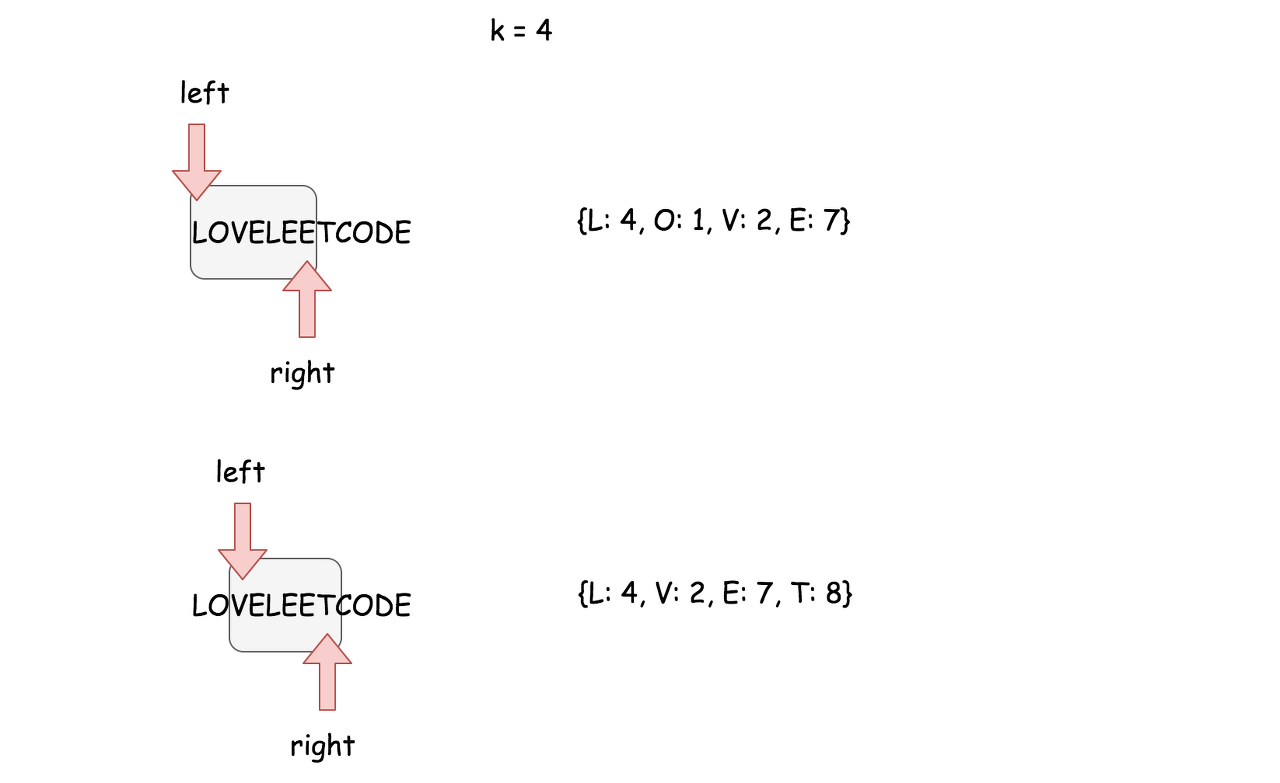
For example, using this hashmap one knows that the rightmost position of character O in "LOVELEE" window is 1 and so one has to move left pointer in the position 1 + 1 = 2 to exclude the character O from the sliding window.
Algorithm
Now one could write down the algortihm.
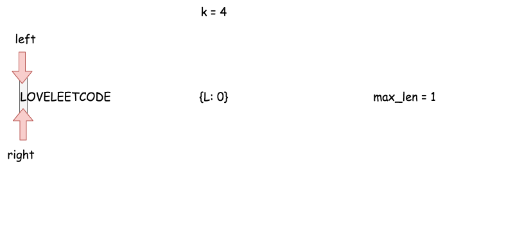
- Return 0 if the string is empty or k is equal to zero.
- Set both set pointers in the beginning of the string left = 0 and right = 0 and init max substring length max_len = 1.
- While right pointer is less than N:
- Add the current character s[right] in the hashmap and move right pointer to the right.
- If hashmap contains k + 1 distinct characters, remove the leftmost character from the hashmap and move the left pointer so that sliding window contains again k distinct characters only.
- Update max_len.
Implementation
1 / 18
class Solution:
def lengthOfLongestSubstringKDistinct(self, s: str, k: int) -> int:
n = len(s)
if n * k == 0:
return 0
left, right = 0, 0
hashmap = defaultdict()
max_len = 1
while right < n:
hashmap[s[right]] = right
right += 1
if len(hashmap) == k + 1:
del_idx = min(hashmap.values())
del hashmap[s[del_idx]]
left = del_idx + 1
max_len = max(max_len, right - left)
return max_len
Complexity Analysis
Do we have here the best possible time complexity \mathcal{O}(N)O(N) as it was for more simple problem with at most two distinct characters?
For the best case when input string contains not more than k distinct characters the answer is yes. It's the only one pass along the string with N characters and the time complexity is \mathcal{O}(N)O(N).
For the worst case when the input string contains n distinct characters, the answer is no. In that case at each step one uses \mathcal{O}(k)O(k) time to find a minimum value in the hashmap with k elements and so the overall time complexity is \mathcal{O}(N k)O(Nk).
-
Time complexity : \mathcal{O}(N)O(N) in the best case of k distinct characters in the string and \mathcal{O}(N k)O(Nk) in the worst case of N distinct characters in the string.
-
Space complexity : \mathcal{O}(k)O(k) since additional space is used only for a hashmap with at most k + 1 elements.
Approach 2: Sliding Window + Ordered Dictionary.
How to achieve \mathcal{O}(N)O(N) time complexity
Approach 1 with a standard hashmap couldn't ensure \mathcal{O}(N)O(N) time complexity.
To have \mathcal{O}(N)O(N) algorithm performance, one would need a structure, which provides four operations in \mathcal{O}(1)O(1) time :
-
Insert the key
-
Get the key and check if the key exists
-
Delete the key
-
Return the first or last added key/ value
The first three operations in \mathcal{O}(1)O(1) time are provided by the standard hashmap, and the forth one - by linked list.
There is a structure called ordered dictionary, it combines behind both hashmap and linked list. In Python this structure is called OrderedDict and in Java LinkedHashMap.
Ordered dictionary is quite popular for interviews. for example, check out the Implementing a LRU Cache question by Google.
Algorithm
Let's use ordered dictionary instead of standard hashmap to trim the algorithm from approach 1 :
- Return 0 if the string is empty or k is equal to zero.
- Set both pointers to the beginning of the string left = 0 and right = 0 and initialize max substring length max_len = 1.
- While right pointer is less than N:
- If the current character s[right] is already in the ordered dictionary hashmap -- delete it, to ensure that the first key in hashmap is the leftmost character.
- Add the current character s[right] in the ordered dictionary and move right pointer to the right.
- If ordered dictionary hashmap contains k + 1 distinct characters, remove the leftmost one and move the left pointer so that sliding window contains again k distinct characters only.
- Update max_len.
Implementation
class Solution:
def lengthOfLongestSubstringKDistinct(self, s: str, k: int) -> int:
n = len(s)
if k == 0 or n == 0:
return 0
left, right = 0, 0
hashmap = OrderedDict()
max_len = 1
while right < n:
character = s[right]
if character in hashmap:
del hashmap[character]
hashmap[character] = right
right += 1
if len(hashmap) == k + 1:
_, del_idx = hashmap.popitem(last = False)
left = del_idx + 1
max_len = max(max_len, right - left)
return max_len
Complexity Analysis
-
Time complexity : \mathcal{O}(N)O(N) since all operations with ordered dictionary : insert/get/delete/popitem (put/containsKey/remove) are done in a constant time.
-
Space complexity : \mathcal{O}(k)O(k) since additional space is used only for an ordered dictionary with at most k + 1 elements.





